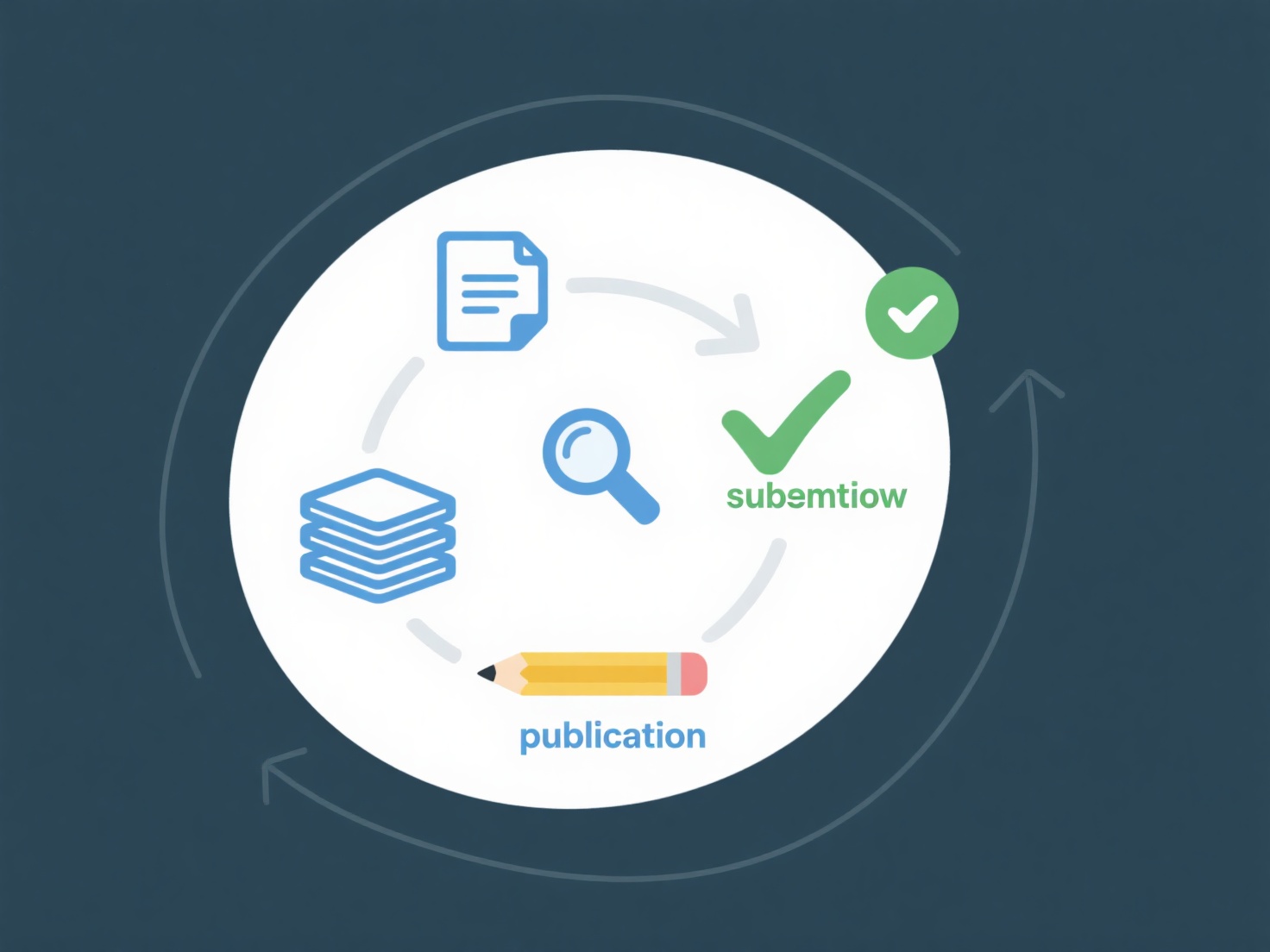
How to understand the publication cycle of a journal?
The publication cycle refers to the chronological process and frequency through which a scholarly journal handles manuscripts from submission to final release, including issue scheduling. Understanding it is crucial for authors and readers to navigate academic timelines effectively.
Key elements include the submission review period, revision rounds, acceptance timelines, production phases, and the frequency of issue releases (e.g., monthly, quarterly). Authors must account for peer review duration, which can range from weeks to months, and publication lags that might extend several months post-acceptance. Scoping reputable sources like journal websites or databases is essential to verify current schedules and avoid outdated information. Factors like journal prestige or submission volume often influence cycle variability and delays.
To comprehend the cycle, first consult the journal’s official "Instructions for Authors" section online for explicit timelines. Review recent issues to confirm publication frequency and dates, and cross-reference academic platforms such as Scopus or CrossRef for metadata. For implementation, estimate potential submission-to-publication delays in research planning; this optimizes timely dissemination and enhances project management. Such understanding benefits researchers by reducing uncertainties and improving strategic decisions.